Java中的IO接口是程序用来进行数据输入输出的接口。数据的输入来源和输出目的地可以是下面的对象:
- 文件
- 管道
- 网络连接
- 内存缓存
- `System.in`, `System.out`,`System.error`(注:Java标准输入、输出、错误输出)
关于普通Java IO的学习,需要掌握下面几点:
- 流的概念
- 流的分类方式(输入流/输出流 字符流/字节流)
- 常见的对象及其作用
- 掌握文件读写/异常处理代码(重要)
## 文件FIle
File类是Java中和平台无关的文件、文件夹的抽象。需要注意的是通过File类不能访问文件本身的内容,如果需要访问文件的内容需要通过输入输出流。File类的常见作用如下:
- 检测文件是否存在
- 读取文件长度
- 重命名或移动文件
- 删除文件
- 检测某个路径是文件还是目录
- 读取目录中的文件列表
**File类有个比较有趣的方法需要提下。File类的list()方法可以列举出当前文件夹下的文件名,而且这个方法可以接收一个过滤器,只显示符合某些规则的文件。**
## 流
在Java IO中,流是一个核心的概念。流从概念上来说是一个连续的数据流。你既可以从流中读取数据,也可以往流中写数据。流与数据源或者数据流向的媒介相关联。在Java IO中流既可以是字节流(以字节为单位进行读写),也可以是字符流(以字符为单位进行读写)。
在Java中按照不同的分类方式可以分为输入流和输出流,字节流和字符流。
Java IO中包含了许多InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer的子类。这样设计的原因是让每一个类都负责不同的功能。这也就是为什么IO包中有这么多不同的类的缘故。各类用途汇总如下:
- 文件访问
- 网络访问
- 内存缓存访问
- 线程内部通信(管道)
- 缓冲
- 过滤
- 解析
- 读写文本 (Readers / Writers)
- 读写基本类型数据 (long, int etc.)
- 读写对象
**一个金典的文件读写列子**
```java
FileOutputStreamfos = null;
try {
//true:**表示在原来文件基础上继续往下写*
fos = new FileOutputStream("file.txt",true);
fos.write(("床前明月光" + System.lineSeparator()).getBytes());
fos.write(("疑是地上霜" + System.lineSeparator()).getBytes());
fos.write(("举头望明月" + System.lineSeparator()).getBytes());
fos.write(("低头思故乡" + System.lineSeparator()).getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("创建文件失败...");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null)
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
FileInputStreamfis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt");
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
inthasRead = 0;
while ((hasRead = fis.read(buff)) > 0) {
Stringcontext = new String(buff, 0, hasRead);
System.out.println(context);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null)
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
```
上面的列子中,关闭流的过程比较麻烦。实际开发过程中建议使用Apache等提供的IO工具类,比如使用`org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils`进行流的关闭。
**缓冲流使用**
`BufferedInputStream`和`BufferedReader`添加了缓冲区,会提升读写效率。普通的流读写时一次写一个字符或字节在文件系统,效率不高。
```java
InputStream is = newFileInputStream("file.txt");
BufferedInputStreambis = new BufferedInputStream(is,1024);
Reader reader = newFileReader("file.txt");
BufferedReaderbufferedReader = new BufferedReader(reader,1024);
```
## 输入输出流体系
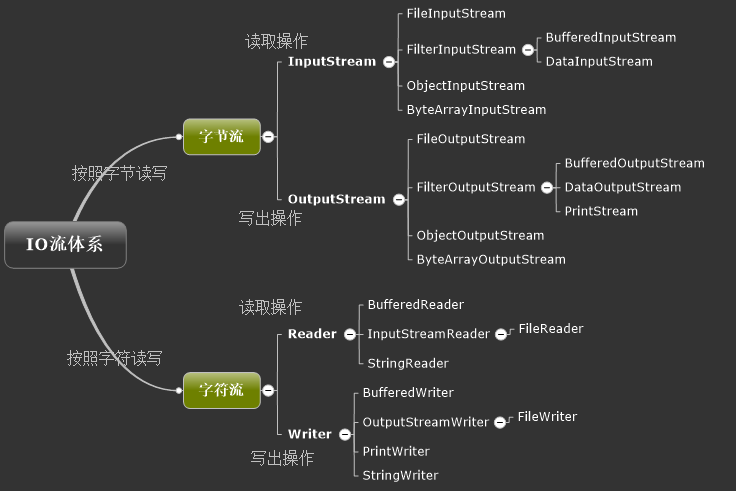
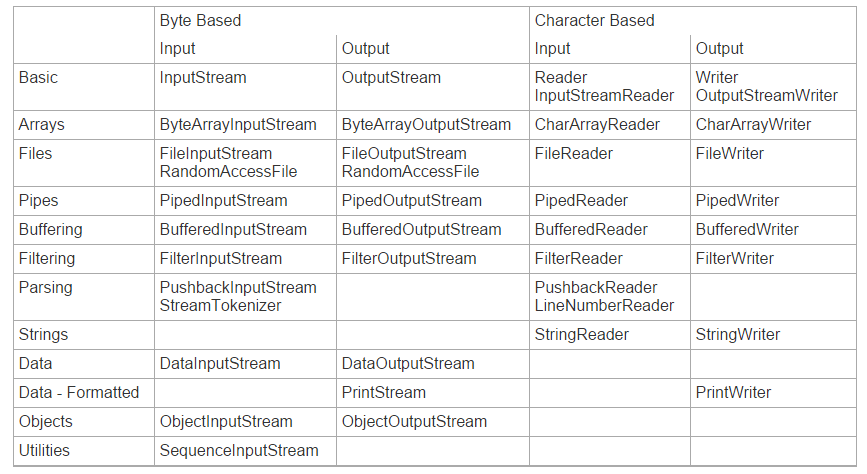
在上图中`PrintStrem`可以用来进行简单方便输出操作。`PrintWriter`功能类似。
一个Reader可以和一个InputStream相结合。如果你有一个InputStream输入流,并且想从其中读取字符,可以把这个InputStream包装到InputStreamReader中。把InputStream传递到InputStreamReader的构造函数中。(装饰器模式的典型使用)
`PushBackInputStream`可以将已经读过的数据重新推回到流里面,从而达到对某些数据重复读的目的。(ServletHttpRequest中body体中的数据只能读一次,使用`PushBackInputStream`是否能解决这个问题??)
通过`Process`类可以读写其他进程的数据:
```java
Process p =System.getRuntimes().exec("java -version");
InputStream is =p.getInputStream();
```
`RandomAcessFile`既可以向文件输入内容,也可以向文件读取内容,还可以随机访问。
**Java IO中的管道为运行在同一个JVM中的两个线程提供了通信的能力**。所以管道也可以作为数据源以及目标媒介。可以通过Java IO中的`PipedOutputStream`和`PipedInputStream`创建管道。一个`PipedInputStream`流应该和一个`PipedOutputStream`流相关联。一个线程通过`PipedOutputStream`写入的数据可以被另一个线程通过相关联的`PipedInputStream`读取出来。
关于基础的IO,暂时就介绍这么多。
## Apache的Commons IO介绍
Apache的Common IO工具包组要包括下面这些工具。
- [Utility classes](http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/javadocs/api-release/index.html?org/apache/commons/io/package-summary.html) - with static methods to perform common tasks
- [Input](http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/javadocs/api-release/index.html?org/apache/commons/io/input/package-summary.html) - useful Input Stream and Reader implementations
- [Output](http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/javadocs/api-release/index.html?org/apache/commons/io/output/package-summary.html) - useful Output Stream and Writer implementations
- [Filters](http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/javadocs/api-release/index.html?org/apache/commons/io/filefilter/package-summary.html) - various implementations of file filters
- [Comparators](http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/javadocs/api-release/index.html?org/apache/commons/io/comparator/package-summary.html) - various implementations of `java.util.Comparator` for files
- [File Monitor](http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/javadocs/api-release/index.html?org/apache/commons/io/monitor/package-summary.html) - a component for monitoring file system events
下面列举几个常用的列子。
**1. IOUtils读取文件**
简单优雅。IOUtils还有很对IO相关的方法,比如copy、write等。大家用的时候可以查看API。使用起来非常简单。
```java
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\一周记录.txt");
String string = IOUtils.toString(fileInputStream, "UTF8");
System.out.println(string);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(fileInputStream);
}
```
**2. FileUtils**
同样的,FileUtils提供了相当丰富的和File交互的API。大家可以按需使用。
```java
File file = new File("D:\\一周记录.txt");
String s = FileUtils.readFileToString(file);
```
因为Commons IO内容较多,具体还是建议参考[官方文档](http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-iohttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/description.html)。当我们自己想要写一个和IO相关的工具类时,不妨
先停下来看看Commons IO中有没类似的。毕竟大厂出的工具包久经考验,不易出错。还能节省我们的开发时间。