##### 一、反爬与反反爬
反爬措施(服务器)
- 通过客户端请求头字段来判断是不是爬虫。
- 通过在url中拼接加密字段,一般通过js动态生成。
- 通过判断一个IP在一个时间段内访问频率。
- 验证码。
- 不直接在页面中显示数据,通过js进行数据渲染。
反反爬措施(你)
- 封装常用请求头,列如:user-agent,Referer。
- 通过 js逆向,或在页面中获得加密字段,。
- 使用IP池,设置爬取策略
- 验证码识别
- 字母验证码,可以通过打码平台识别/自己识别,再输入。
- 滑动/点击验证码,可通过打码平台识别位置后,通过selenium模拟人工滑动/点击,进行验证。
- js渲染可通过以下方法获取数据
- 有些网站数据放置在js代码中,例如36kr。
- 通过selenium+phantomjs(无界面浏览器)、selenium+chrome来获取数据
- 找到数据来源的接口(ajax接口)
- splash获取数据。*Splash*是一个javascript渲染服务。。
##### 二、ajax
###### 1、什么是ajax
Ajax 不是一种新的编程语言,而是一种用于创建更好更快以及交互性更强的Web应用程序的技术。
使用 JavaScript 向服务器提出请求并处理响应而不阻塞用户核心对象XMLHttpRequest。通过这个对象,您的 JavaScript 可在不重载页面的情况与 Web 服务器交换数据,即在不需要刷新页面的情况下,就可以产生局部刷新的效果。Ajax 在浏览器与 Web 服务器之间使用异步数据传输(HTTP 请求),这样就可使网页从服务器请求少量的信息,而不是整个页面。Ajax可使因特网应用程序更小、更快,更友好。
总结下来:ajax是通过XMLHttpRequest对象,在不刷新页面的情况下异步发送请求,接受响应,的一种网络技术。
##### 三、selenium与浏览器驱动安装。
###### 1、安装 selenium 模块
```
pip install selenium
```
###### 2、下载浏览器驱动并且安装。
下载 chromedrive,首先需要查看自己的浏览器版本
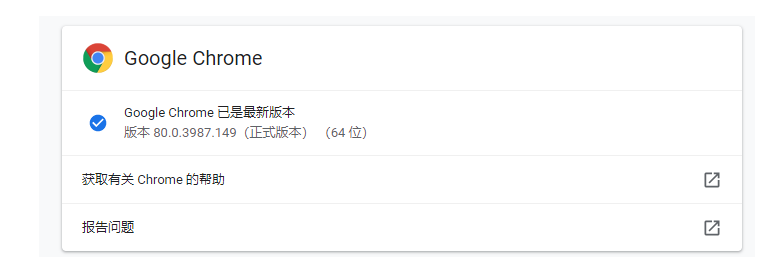
chromedrive下载地址:https://chromedriver.storage.googleapis.com/index.html?path=80.0.3987.106/
phantomjs下载地址:https://bitbucket.org/ariya/phantomjshttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/downloads/phantomjs-2.1.1-windows.zip
下载完成后解压,移动到python.exe所在的目录,你也可以进行单独环境变量配置,不过这种方法是最简单的
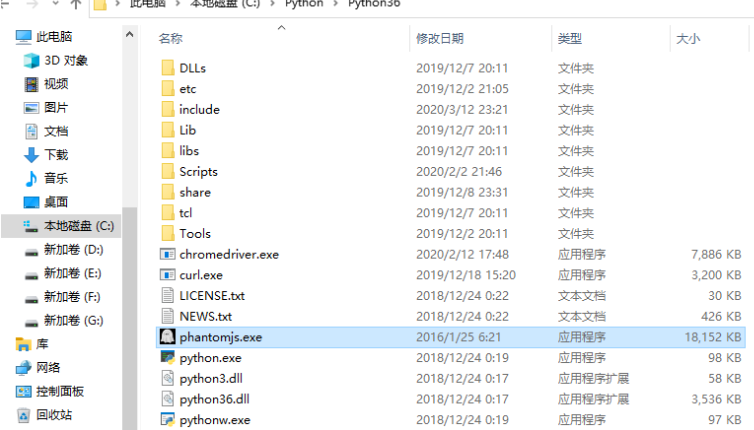
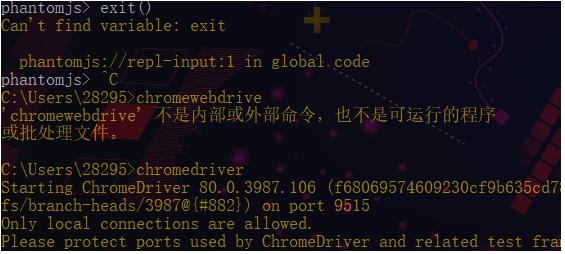
是否成功,在cmd命令行中输入相关命令
##### 四、selenium简单使用
###### 4.1、常用方法如下
```
from selenium import webdriver
chrome = webdriver.Chrome()
# 访问url
chrome.get('https://www.baidu.com')
# 元素选择
input_1 = chrome.find_element_by_id('kw') # 通过id选择
input_2 = chrome.find_element_by_xpath("//input[@id='su']") # 通过xpath
input_3 = chrome.find_element_by_css_selector('#su') # 通过css选择器
input_4 = chrome.find_element_by_class_name('bg s_btn') # 通过类名
# 往输入框内发送内容,并且点击
input_1.send_keys('spider')
button = chrome.find_element_by_xpath('//input[@id="su"]')
# 获取某对象的png bytes数据
content_bytes = button.screenshot_as_png
# 获取元素的位置
print(button.location)
button.click()
# 全屏截图
chrome.save_screenshot('1.png')
# 元素大小
print(button.size)
chrome.close()
# 关闭选项卡
chrome.close()
# 退出浏览器
chrome.quit()
```
###### 4.2、selenium提取cookies字典
```
from selenium import webdriver
chrome = webdriver.Chrome()
chrome.get('http://www.baidu.com')
cookies = chrome.get_cookies()
cok_dic = {i.get('name'): i.get('value') for i in cookies}
print(cok_dic)
chrome.close()
chrome.quit()
```
###### 4.3、selenium中的三种等待
代码执行的速度是非常快的,但是我们通过selenium+浏览器驱动去驱动一个浏览器执行某些动作,但是浏览器执行的速度很慢。我们进行数据提取时,浏览器页面并没有加载完毕,我们可能会提取不到数据,所以需要设置等待。
```
强制等待:shitime.sleep(1) #程序暂停1秒
隐式等待:chrome.implicitly_wait(5) #最多等待5秒,在5秒内,加载完成就不会报错。
显示等待:指定时间情况下,指定某些元素或者状态是否加载完成。加载完成就不会报错。
```
```
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By #通过什么方式判断:id、xpath、cssselect、等
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
next_page = WebDriverWait(self.browser, 5).until(
EC.presence_of_element_located((By.XPATH, '/https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[contains(@class,"paginator")]/a[last()]'))) #等待a标签是否加载成功。
next_url = next_page.get_attribute('href')
#EC这个类中提供了很多判断条件,下面是常用判断条件
title_is #title标签内容是..
title_contains #title标签包含。
presence_of_element_located #元素加载完成
visibility_of_element_located #元素可视
text_to_be_present_in_element #元素内的内容加载完成
element_to_be_clickable #元素可点击
element_to_be_selected #元素可选择
```
#### 五、相关案例
##### 5.1、豆瓣图书
```
from selenium import webdriver
import time
import random
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from lxml import etree
import xlwt
class Douband():
def __init__(self, kw, page):
self.base_url = 'https://book.douban.com/'
self.browser = webdriver.Chrome()
self.page_url = ''
self.kw = kw
self.page = page
self.cont_list = []
def get_index(self, url):
self.browser.get(url)
try:
next_page = WebDriverWait(self.browser, 5).until(
EC.presence_of_element_located((By.XPATH, '/https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[contains(@class,"paginator")]/a[last()]')))
next_url = next_page.get_attribute('href')
self.page_url = next_url
return self.browser.page_source
except Exception:
self.browser.quit()
def parser_index(self, content):
html = etree.HTML(content)
item_list = html.xpath('/https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[contains(@class,"sc-bZQynM" )]')
for item in item_list:
title = item.xpath('./https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[@class="detail"]https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[@class="title"]/a/text()')
rating = item.xpath('./https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[@class="detail"]https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[contains(@class,"rating")]/span[2]/text()')
times = item.xpath('./https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[@class="detail"]https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[contains(@class,"rating")]/span[3]/text()'),
info = item.xpath('./https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[@class="detail"]https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[@class="meta abstract"]/text()'),
item = {
'title': title[0] if title else None,
'rating': rating[0] if rating else None,
'times': times[0] if times else None,
'info': info[0] if info else None,
}
print(item)
self.cont_list.append(item)
def search(self):
self.browser.get(self.base_url)
self.browser.find_element_by_id('inp-query').send_keys(self.kw)
time.sleep(random.random())
self.browser.find_element_by_xpath('/https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/div[@class="inp-btn"]/input').click()
def write_to_excel(self, filename, sheetname):
# 创建workbook
file = xlwt.Workbook()
# 添加sheet表
sheet = file.add_sheet(sheetname)
# 设置表头
head = [i for i in self.cont_list[0].keys()]
for i in range(len(head)):
sheet.write(0, i, head[i])
# 写内容
i = 1
for item in self.cont_list:
for j in range(len(head)):
sheet.write(i, j, item[head[j]])
i += 1
# 保存
file.save(filename)
print('写入excle成功!')
def run(self):
self.search()
count = 0
self.page_url = self.browser.current_url
while count < self.page:
content = self.get_index(self.page_url)
self.parser_index(content)
count += 1
self.browser.quit()
self.write_to_excel('python.xls', 'book')
if __name__ == '__main__':
db = Douband('python', 10)
db.run()
```
##### 5.2、腾讯招聘
```
import requests
from jsonpath import jsonpath
from excle_wirte import ExcelUtils
import os
def get_content(url):
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/80.0.3987.149 Safari/537.36',
'referer': 'https://careers.tencent.com/search.html'
}
res = requests.get(url, headers=headers).json()
jp = jsonpath(res, '$.*.Posts.*')
print(jp)
return jp
def write_excel(filename, item_list, sheetname):
if not os.path.exists(filename):
ExcelUtils.write_to_excel(filename, item_list, sheetname)
else:
ExcelUtils.append_to_excel(filename, item_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
base_url = 'https://careers.tencent.com/tencentcareer/api/post/Query?timestamp=1585401795646&countryId=&cityId=&bgIds=&productId=&categoryId=&parentCategoryId=&attrId=&keyword=&pageIndex={}&pageSize=20&language=zh-cn&area=cn'
for i in range(1, 11):
content = get_content(base_url.format(i))
write_excel('tencent.xls',content,'hr')
```
###### 在这里用到了写入excel的一些方法,我这里直接引用了别人封装的方法。
```
import xlwt
import xlrd
from xlutils.copy import copy as C
class ExcelUtils(object):
@staticmethod
def write_to_excel(filename, item_list, sheetname):
try:
# 创建workbook
workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8')
# 给工作表添加sheet表单
sheet = workbook.add_sheet(sheetname)
# 设置表头
head = []
for i in item_list[0].keys():
head.append(i)
# print(head)
# 将表头写入excel
for i in range(len(head)):
sheet.write(0, i, head[i])
# 写内容
i = 1
for item in item_list:
for j in range(len(head)):
sheet.write(i, j, item[head[j]])
i += 1
# 保存
workbook.save(filename)
print('写入excle成功!')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('写入失败!')
@staticmethod
def append_to_excel(filename, item_list):
# 打开excle文件
work_book = xlrd.open_workbook(filename)
# 获取工作表中的所有sheet表单名称
sheets = work_book.sheet_names()
# 获取第一个表单
work_sheet = work_book.sheet_by_name(sheets[0])
# 获取已经写入的行数
old_rows = work_sheet.nrows
# 获取表头的所有字段
keys = work_sheet.row_values(0)
# 将xlrd对象转化成xlwt,为了写入
new_work_book = C(work_book)
# 获取表单来添加数据
new_sheet = new_work_book.get_sheet(0)
i = old_rows
for item in item_list:
for j in range(len(keys)):
new_sheet.write(i, j, item[keys[j]])
i += 1
new_work_book.save(filename)
print('追加成功!')
```