Gesture在 ViewGroup中使用
GestureDetector类可以让我们快速的处理手势事件,如点击,滑动等。
使用GestureDetector分三步:
1. 定义GestureDetector类
2. 初始化手势类,同时设置手势监听
3. 将touch事件交给gesture处理
先来了解一下如何使用,后面会有示例:
package com.example.y2222.myview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.GestureDetector;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
/**
* Created by raise.yang on 2016/06/29.
*/
public class GestureDemoView extends LinearLayout {
//1,定义GestureDetector类
private GestureDetector m_gestureDetector;
public GestureDemoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public GestureDemoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//设置为可点击
setClickable(true);
//2,初始化手势类,同时设置手势监听
m_gestureDetector = new GestureDetector(context, onGestureListener);
//双击监听-一般很少用到
m_gestureDetector.setOnDoubleTapListener(onDoubleTapListener);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//3,将touch事件交给gesture处理
m_gestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
//初始化手势监听对象,使用GestureDetector.OnGestureListener的实现抽象类,因为实际开发中好多方法用不上
private final GestureDetector.OnGestureListener onGestureListener = new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener() {
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onSingleTapUp() ");
return super.onSingleTapUp(e);
}
@Override
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onLongPress() ");
super.onLongPress(e);
}
@Override
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onScroll() distanceX = " + distanceX);
return super.onScroll(e1, e2, distanceX, distanceY);
}
@Override
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onFling() velocityX = " + velocityX);
return super.onFling(e1, e2, velocityX, velocityY);
}
@Override
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onShowPress() ");
super.onShowPress(e);
}
@Override
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onDown() ");
return super.onDown(e);
}
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onDoubleTap() ");
return super.onDoubleTap(e);
}
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onDoubleTapEvent() ");
return super.onDoubleTapEvent(e);
}
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onSingleTapConfirmed() ");
return super.onSingleTapConfirmed(e);
}
@Override
public boolean onContextClick(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onContextClick() ");
return super.onContextClick(e);
}
};
private final GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener onDoubleTapListener = new GestureDetector.OnDoubleTapListener() {
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onSingleTapConfirmed() OnDoubleTapListener");
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onDoubleTap() OnDoubleTapListener");
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onDoubleTapEvent() OnDoubleTapListener");
return false;
}
};
}
注意:setClickable(true);一定要加,不然只会收到下例3个事件,被这个整了好长时间才找到原因.(⊙﹏⊙)b
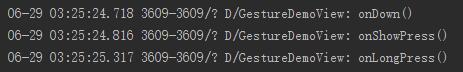
对于单击,双击,拖动等事件调用见下图:
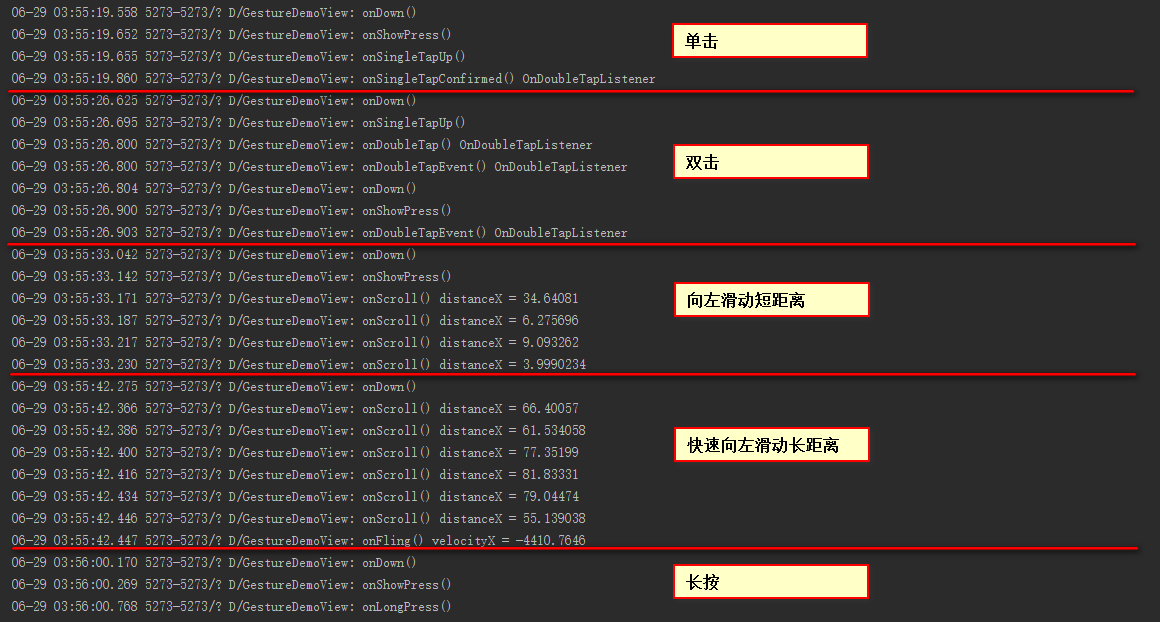
根据上图,每个方法大致都调用了,说明几个容易弄混的回调方法
1. onScroll()
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY)
e1:滑动事件的起点(也就是说onDown()的时候)
e2:当前滑动位置点(手指的位置)
distanceX:上次滑动(调用onScroll)到这次滑动的X轴的距离px,不是e1点到e2点的X轴的距离
distanceY:上次滑动(调用onScroll)到这次滑动的Y轴的距离px,不是e1点到e2点的Y轴的距离
2. onFling()
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY)
e1:拖动动事件的起点(也就是说onDown()的时候)
e2:onFling()调用时,手指的位置
velocityX:X轴上每秒滑动像素值
velocityY:Y轴上每秒滑动像素值
注意:当拖动速率velocityX或velocityY超过ViewConfiguration.getMinimumFlingVelocity()最小拖动速率时,才会调用onFling(),也就是如果只拖动一点,或是慢慢的拖动,是不会触发该方法。
对应源码:
if ((Math.abs(velocityY) > mMinimumFlingVelocity)
|| (Math.abs(velocityX) > mMinimumFlingVelocity)){
handled = mListener.onFling(mCurrentDownEvent, ev, velocityX, velocityY);
}
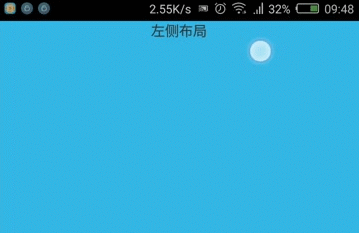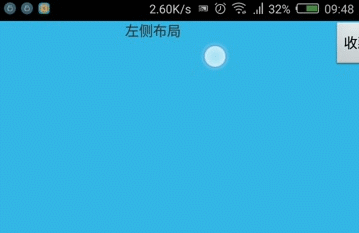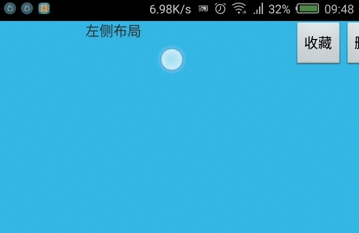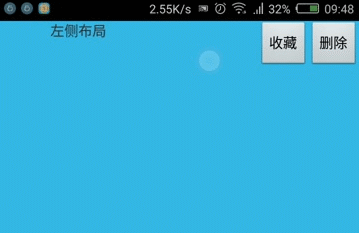
实践:使用GestureDetector实现左滑删除
在很多ListView中都有该效果,现在自己实现下,顺便熟悉GestureDetector的使用。
效果图:
GestureDemoView.java:
package com.example.y2222.myview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.GestureDetector;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import com.example.y2222.myapplication.R;
/**
* Created by raise.yang on 2016/06/29.
*/
public class GestureDemoView extends LinearLayout {
//1,定义GestureDetector类
private GestureDetector m_gestureDetector;
private int m_max_scrollX;
public GestureDemoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public GestureDemoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//设置为可点击
setClickable(true);
//2,初始化手势类,同时设置手势监听
m_gestureDetector = new GestureDetector(context, onGestureListener);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.view_gesture, this);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//3,将touch事件交给gesture处理
m_gestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {
// GestureDetector没有处理up事件的方法,只能在这里处理了。
int scrollX = getScrollX();
if (scrollX > m_max_scrollX / 2) {
show_right_view();
} else {
hide_right_view();
}
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
//测量子view的宽高,?不测量,右侧布局会不显示,这里有点疑问
measureChild(getChildAt(i), widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (i == 1) {
m_max_scrollX = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredWidth();
}
}
}
//初始化手势监听对象,使用GestureDetector.OnGestureListener的实现抽象类,因为实际开发中好多方法用不上
private final GestureDetector.OnGestureListener onGestureListener = new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener() {
@Override
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onScroll() distanceX = " + distanceX + " getScrollX = " + getScrollX() + " max_scrollX = " + m_max_scrollX);
int scrollX = getScrollX();
int minScrollX = -scrollX;
int maxScrollY = m_max_scrollX - scrollX;
// 对滑动的距离边界控制
if (distanceX > maxScrollY) {
distanceX = maxScrollY;
} else if (distanceX < minScrollX) {
distanceX = minScrollX;
}
scrollBy((int) distanceX, 0);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY) {
Log.d("GestureDemoView", "onFling() velocityX = " + velocityX);
if (velocityX < 0) {
//快速向左滑动
show_right_view();
} else {
hide_right_view();
}
return super.onFling(e1, e2, velocityX, velocityY);
}
};
private void show_right_view() {
scrollTo(m_max_scrollX, 0);
}
private void hide_right_view() {
scrollTo(0, 0);
}
}
view_gesture.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center" android:text="左侧布局"/> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="收藏"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="删除"/> </LinearLayout> </merge>
xml文件中根标签使用<merge>,可减少一层view树嵌套,并且使用getChildCount()能得到我们想要的子view个数。
关于<merge>标签的使用,详见郭神的blog:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/43376527
实现也很简单,在scroll和fling的时候,得到滑动距离或滑动速度,再调用view自己的scrollTo()或scrollBy()滑动内部元素即可。
从效果图中,当滑动到一半松手时,立即滑动到最左边,完全没有动画,这样的体验很差,所以还需优化。关于滑动时增加动画效果,可以使用Scroller类完成,准备下期补上。
Gesture在 View中使用
和在viewgroup中一样,在view中,同样是经过三步来实现:
1. 定义GestureDetector类
2. 初始化手势类,同时设置手势监听
3. 将touch事件交给gesture处理
举个荔枝:
做了一个小球跟随手指移动的效果,先绘制小球,当手指放在小球上滑动时,会调用onScroll(),在这个方法中,修改圆心的位置进行重绘,这样小球就能移动了。
这里有2个难点:
1. 如何判断手指落在了小球上;
2. 滑动到边界时,不能超过边界;
效果图:

GestureView.java代码:
package com.example.y2222.myview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.GestureDetector;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
/**
* Created by raise.yang on 2016/07/05.
*/
public class GestureView extends View {
private GestureDetector m_gestureDetector;
private Paint m_paint;
//小球的中心点
private float centerX;
private float centerY;
//小球的半径
private int radius;
//是否touch在小球上
private boolean touch_bool;
public GestureView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public GestureView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
// 初始画笔
m_paint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
m_paint.setColor(getResources().getColor(android.R.color.holo_blue_light));
//设置为可点击
setClickable(true);
//2,初始化手势类,同时设置手势监听
m_gestureDetector = new GestureDetector(context, onGestureListener);
radius = 50;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//3,将touch事件交给gesture处理
m_gestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event);
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
//判断手指落在了小球上
if (getDistanceByPoint((int) centerX, (int) centerY, (int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY()) < radius) {
touch_bool = true;
} else {
touch_bool = false;
}
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
// 默认圆心在中心点
if (w > 0) {
centerX = w / 2;
}
if (h > 0) {
centerY = h / 2;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY, radius, m_paint);
}
GestureDetector.OnGestureListener onGestureListener = new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener() {
@Override
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY) {
if (touch_bool) {
centerY -= distanceY;
centerX -= distanceX;
//处理边界问题
if (centerX < radius) {
centerX = radius;
} else if (centerX > getWidth() - radius) {
centerX = getWidth() - radius;
}
if (centerY < radius) {
centerY = radius;
} else if (centerY > getHeight() - radius) {
centerY = getHeight() - radius;
}
//修改圆心后,通知重绘
postInvalidate();
}
return true;
}
};
/**
* 计算两点间的距离
*/
private int getDistanceByPoint(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
double temp = Math.abs((x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1) - (y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1));
return (int) Math.sqrt(temp);
}
}
在处理问题1时,我设置了一个boolean值,在用户触摸的时候去判断,当前点和圆心点的距离是否小于半径,若小于,说明在圆内。这样在滑动的时候,就去判断一下,是否需要滑动小球。
控制边界,其实就是控制圆心点的坐标,只要保证落在(radius,radius),(getWidth()-radius,getHeight()-radius)两点矩形中即可。