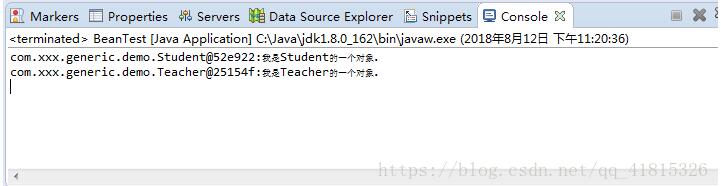
说明:
其作用是减少层与层之间的依赖。
实现步骤:
编写2个类(Student,Teacher)再编写beans.properties文件,接着编写BeanFactory类,最后编写测试类BeanTest。
参考代码如下:
/**
*beans.properties文件的内容(位于与src平级的config资源包下)
*/
Student=com.xxx.generic.demo.Student
Teacher=com.xxx.generic.demo.Teacher
/**
*BeanFactory类的参考代码
*/
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class BeanFactory {
private BeanFactory() {
}
private static Map<String, String> beans = new HashMap<>();
static {
InputStream is = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("beans.properties");
Properties prop = new Properties();
try {
prop.load(is);
Enumeration<String> keys = (Enumeration<String>) prop.propertyNames();
while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = keys.nextElement();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
beans.put(key, value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
T t = null;
String className = clazz.getSimpleName();
Set<String> keys = beans.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
if (key.equals(className)) {
String value = beans.get(key);
try {
t = (T) Class.forName(value).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
}
}
return t;
}
}
/**
*BeanTest类参考代码
*/
public class BeanTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = BeanFactory.getBean(Student.class);
System.out.println(s + ":我是" + s.getClass().getSimpleName() + "的一个对象。");
Teacher t = BeanFactory.getBean(Teacher.class);
System.out.println(t + ":我是" + t.getClass().getSimpleName() + "的一个对象。");
}
}
运行结果如下: