/* Navicat Premium Data Transfer Source Server : win-local Source Server Type : MySQL Source Server Version : 50737 Source Host : localhost:3306 Source Schema : db0 Target Server Type : MySQL Target Server Version : 50737 File Encoding : 65001 Date: 24/04/2022 20:27:41 */ SET NAMES utf8mb4; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for user -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`; CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `age` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
不用Springboot依赖,引入mysql驱动依赖、spring-beans、spring-jdbc、Spring-context依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.46</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring jdbc 依赖spring-tx -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>首先在resources目录下创建一个spring.xml文件,Spring框架为了声明自己的Xml规范,在<beans>标签里定义了spring 框架指定模块的协议配置, 我们可以通过Index of /schema访问spring框架的所有模块包,各模块包含了不同版本的xsd文件。

点击进入context目录,查看xsd文件:

比如我要通过xml的形式配置一个bean, 需要在beans标签中声明 xmln的值为:
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
如果我想用spring的context模块,那么需要声明
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
同时在xsi: schemeLocation里添加context的url和spring-contxt.xsd的url:
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
例如我创建一个能在xml中使用spring-beans模块,spring-txt模块,spring-context模块的配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
">
</beans>如果没有在beans标签里声明协议,那么在配置bean时会出现找不到指定标签的问题。
在spring.xml文件中添加配置事务配置,使用 annotation-driven 属性开启事务启动,
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true" mode="proxy"/>
proxy-target-class默认为false, mode默认模式为proxy,可不用配置,待会从源码角度分析不同模式的事务开启。
接着配置transactionManager, 指定class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true" mode="proxy"/>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="ds"/>
</bean>DataSourceTransactionManager里包含了DataSource属性配置:
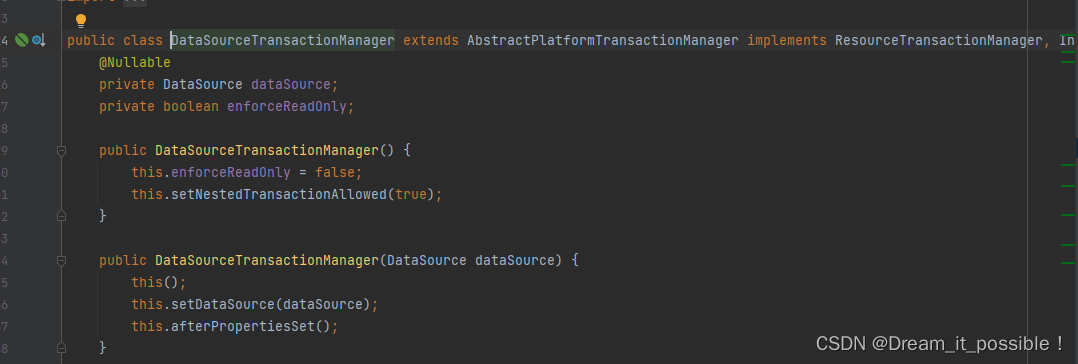
因此我们需要接着配置数据源bean 别名为
<bean id="ds" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db0?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="5"/>
<property name="maxIdle" value="2"/>
<property name="maxTotal" value="100"/>
</bean>接着给Service配置一个bean, 引用dataSource数据源。
<!-- 配置bean,指定数据源-->
<bean id="userService" class="service.UserService">
<property name="dataSource" ref="ds"/>
</bean>通过dataSouce bean注入JDBCTemplate, 添加一个update(int id,String name)方法, 类上添加@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)。
package service;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class UserService {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
public String getUserName(int id) {
return jdbcTemplate.query("select * from db0.user where id= ?", rs -> rs.next() ? rs.getString(2) : "", new Object[]{id});
}
public void updateUser(int id, String name) {
jdbcTemplate.update(" update user set name =? where id= ?", new Object[]{name, id});
// throw new RuntimeException("error!");
}
}使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类加载spring.xml文件
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import service.UserService;
public class UserServiceTests {
@Test
public void testTransaction() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
String name = userService.getUserName(1);
System.out.println("名字:"+name);
userService.updateUser(1, "bing");
String updateName = userService.getUserName(1);
System.out.println("更新后的名字:" + updateName);
}
}数据库一条记录:
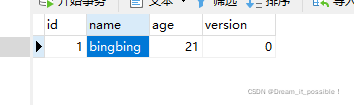
update方法里放开//throw new RuntimeException("error!"); 注释,执行后

数据库里的记录没有修改,@Tranasctional注解生效。
重新执行后,观察结果

数据库也更新过来了。

前面的篇幅从xml的配置形式解释了Transaction集成过程,为什么要从xml形式入手transaction, 是为了后面阅读Spring-tx源码做准备。
根据spring.xml文件里配置的tx:annitation-driven 关键字在Spring框架里全局搜索,找到目标类TxNamespaceHandler。位于spring-tx模块中的 org.springframework.transaction.config包下。

/*
* Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.transaction.config;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
/**
* {@code NamespaceHandler} allowing for the configuration of
* declarative transaction management using either XML or using annotations.
*
* <p>This namespace handler is the central piece of functionality in the
* Spring transaction management facilities and offers two approaches
* to declaratively manage transactions.
*
* <p>One approach uses transaction semantics defined in XML using the
* {@code <tx:advice>} elements, the other uses annotations
* in combination with the {@code <tx:annotation-driven>} element.
* Both approached are detailed to great extent in the Spring reference manual.
*
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0
*/
public class TxNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static final String TRANSACTION_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE = "transaction-manager";
static final String DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME = "transactionManager";
static String getTransactionManagerName(Element element) {
return (element.hasAttribute(TRANSACTION_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE) ?
element.getAttribute(TRANSACTION_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE) : DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME);
}
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("advice", new TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser());
// 注册事务
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("jta-transaction-manager", new JtaTransactionManagerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}找到了annotation-driven, 这个地方创建了一个AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser实例。
AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser 类的作用是解析spring.xml里的配置<tx:annotation-driven>标签,并根据配置的mode选择不同的模式取创建Transaction的整个初始化流程,此处也就是整个架Transaction架构的开始地方。

Spring事务注册的模式为动态代理模式,具体实现有2种: aspectj和proxy,可通过配置来选择使用那种形式的事务注册, 如果不配置mode那么使用默认的proxy形式创建,如果我们要使用aspectj模式开启事务,那么就配置mode="aspectj"。
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" mode="aspectj">
我们可以看到Spring事务的开启是默认是以AOP为基础的。
AopAutoProxyConfigurer 的configureAutoProxyCreator方法注册了3个Bean, 该3个Bean 是驱动Spring 事务架构的核心支柱,分别是TransactionAttributeSource、TransactionInterceptor、TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor。
private static class AopAutoProxyConfigurer {
public static void configureAutoProxyCreator(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
String txAdvisorBeanName = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME;
if (!parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName)) {
Object eleSource = parserContext.extractSource(element);
// Create the TransactionAttributeSource definition.
RootBeanDefinition sourceDef = new RootBeanDefinition(
"org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource");
sourceDef.setSource(eleSource);
sourceDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
String sourceName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(sourceDef);
// Create the TransactionInterceptor definition.
RootBeanDefinition interceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(TransactionInterceptor.class);
interceptorDef.setSource(eleSource);
interceptorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registerTransactionManager(element, interceptorDef);
interceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
String interceptorName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(interceptorDef);
// Create the TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor definition.
RootBeanDefinition advisorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor.class);
advisorDef.setSource(eleSource);
advisorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("adviceBeanName", interceptorName);
if (element.hasAttribute("order")) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("order", element.getAttribute("order"));
}
// 事务通知器 transaction advisor, 基于AOP实现的advisor
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName, advisorDef);
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), eleSource);
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(sourceDef, sourceName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(interceptorDef, interceptorName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(advisorDef, txAdvisorBeanName));
parserContext.registerComponent(compositeDef);
}
}
}其中TransactionInterceptor是Spring事务的目标方法的增强,通过代理完成Spring 事务的提交、异常处理和回滚。

TransactionInterceptor是Spring 事务对目标方法的增强器,说简单点就是一层代理,基于Aop实现,实现了spring-aop的Advice接口,同时实现了IntializingBean和BeanFactoryAware接口,只要有事务的执行,那么目标方法的调用类在invoke()方法会生成一个代理对象,通过invoke()方法对目标调用方法进行增强。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
/**
* Implement this method to perform extra treatments before and
* after the invocation. Polite implementations would certainly
* like to invoke {@link Joinpoint#proceed()}.
* @param invocation the method invocation joinpoint
* @return the result of the call to {@link Joinpoint#proceed()};
* might be intercepted by the interceptor
* @throws Throwable if the interceptors or the target object
* throws an exception
*/
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}TransactionInterceptor的invoke()实现:
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}Spring 创建事务的方式有二种: 声明式事务和编程式事务, 我们可以通过分析一种理解核心流程和原理即可。
进入invokeWithinTransaction()方法直接看声明式事务执行过程的源代码:
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 创建事务
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 根据指定异常进行回滚。
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}invokeWithinTransaction方法做了哪些事?
1)通过createTransactionIfNecessary方法创建一个事务,相当于此处开启一个事务。
2)invocation.proceedWithInvocation() 执行目标方法调用。
3) 如果出现异常,那么completeTransactionAfterThrowing处理异常。
4) 在finally 清除掉transaction相关的信息,同时在commitTransactionAfterReturning 提交事务。

我们可以从上面的源码中发现通过transactionManager执行回滚操作。
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());