在JavaScript中,经常会通过call / apply / bind 函数来改变this的指向,详情可看一文带你了解this指向,今天我们来研究下这三个函数的实现。
call()函数是什么?
call() 方法使用一个指定的 this 值和单独给出的一个或多个参数来调用一个函数。也就是说call() 改变了this指向并执行了函数。
func.call(thisArg, arg1, arg2, ...) // thisArg为在 func 函数运行时使用的 this 值 // arg1, arg2等为指定的参数列表 // 其返回值为调用有指定 this 值和参数的函数的结果
一般来说,我们要模拟实现call,可以分为以下几个步骤:
以下就是call()方法实现的流程图:
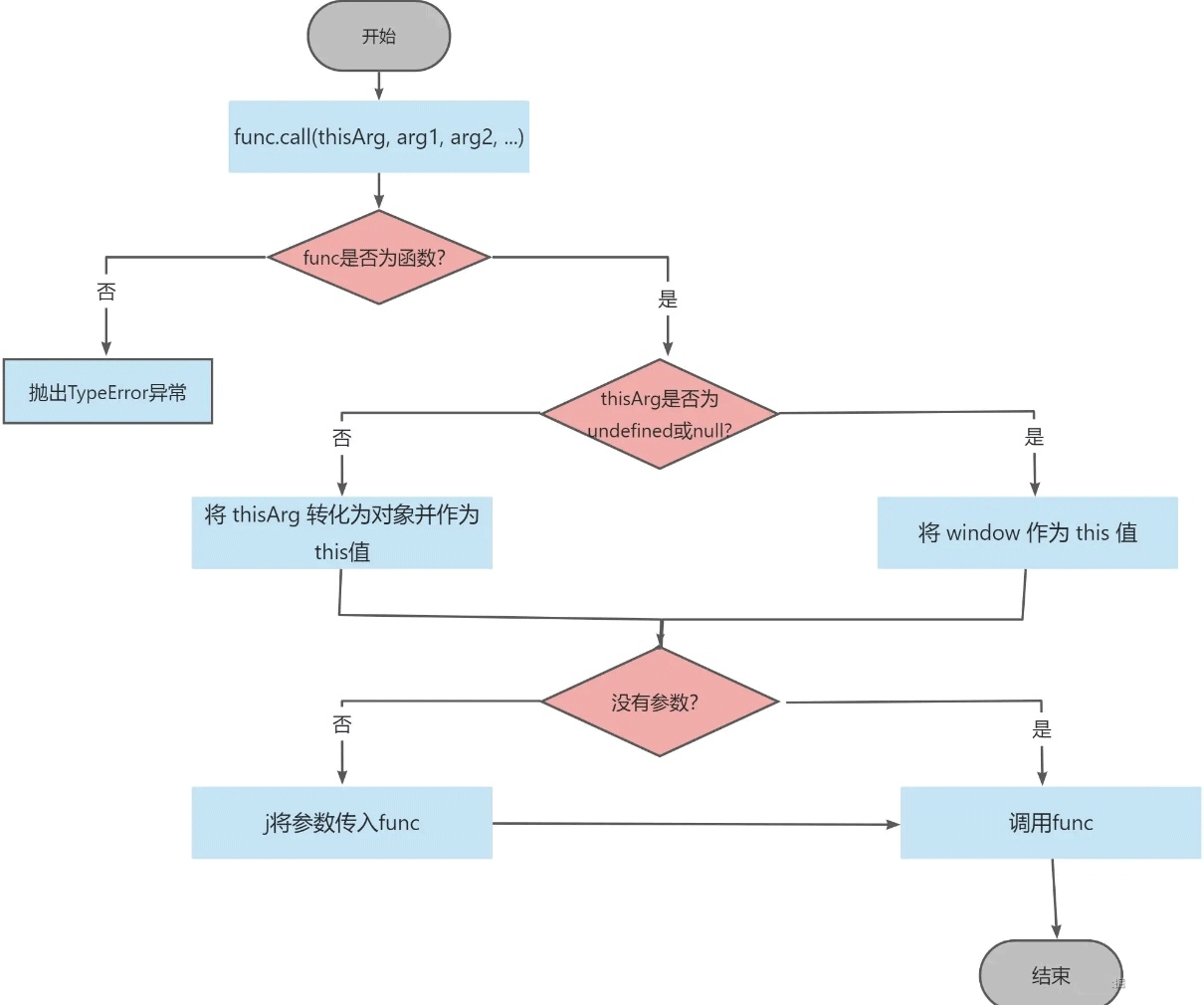
Function.prototype.call = function (thisArg, ...argsArray) {
if (typeof this !== "function") {
throw new TypeError(
"Function.prototype.call was called on which is not a function"
);
}
if (thisArg === undefined || thisArg === null) {
thisArg = window;
} else {
thisArg = Object(thisArg);
}
// 将 func 放入 thisArg 内,这样在调用 thisArg[func] 时 this 自然就指向了 thisArg
const func = Symbol("func");
thisArg[func] = this;
let result;
if (argsArray.length) {
result = thisArg[func](...argsArray);
} else {
result = thisArg[func]();
}
delete thisArg[func];
return result;
};apply()函数是什么?
apply() 方法调用一个具有给定 this 值的函数,以及以一个数组(或一个类数组对象)的形式提供的参数。同call()的功能,改变this指向的同时执行了函数。
func.apply(thisArg, [argsArray]); // thisArg为在 func 函数运行时使用的 this 值 // arg1, arg2等为指定的参数列表 // 其返回值为调用有指定 this 值和参数的函数的结果
apply()方法实现的流程基本与call的实现流程没有太多差异,只需要对函数参数数组进行判断展开即可。
以下是apply()函数的流程图:
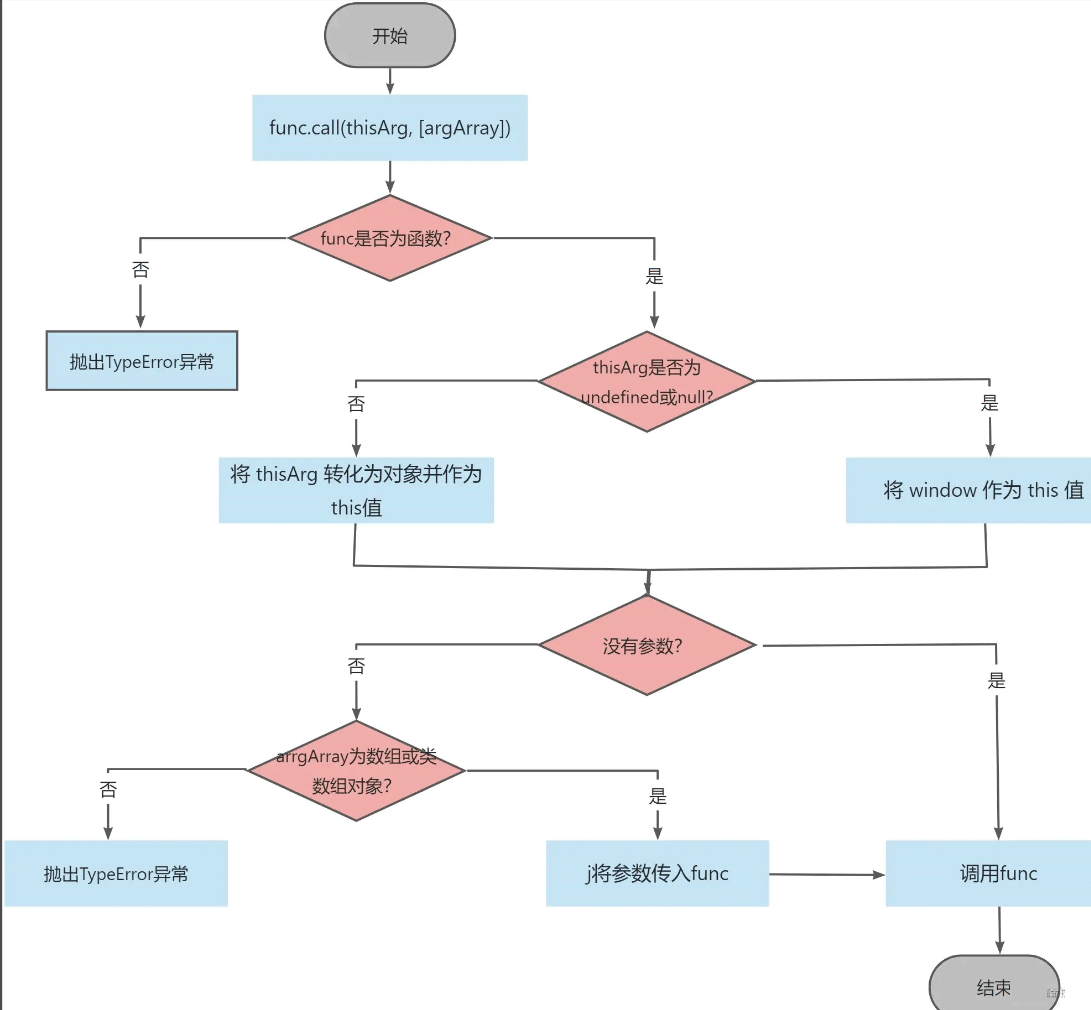
Function.prototype.apply = function (thisArg, argsArray) {
if (typeof this !== "function") {
throw new TypeError(
"Function.prototype.apply was called on which is not a function"
);
}
if (thisArg === undefined || thisArg === null) {
thisArg = window;
} else {
thisArg = Object(thisArg);
}
// 将 func 放入 thisArg 内,这样在调用 thisArg[func] 时 this 自然就指向了 thisArg
const func = Symbol("func");
thisArg[func] = this;
let result;
if (argsArray && typeof argsArray === "object" && "length" in argsArray) {
// 此处使用 Array.from 包裹让其支持形如 { length: 1, 0: 1 } 这样的类数组对象,直接对 argsArray 展开将会执行出错
result = thisArg[func](...Array.from(argsArray));
} else if (argsArray === undefined || argsArray === null) {
result = thisArg[func]();
} else {
throw new TypeError("CreateListFromArrayLike called on non-object");
}
delete thisArg[func];
return result;
};