有时会遇到这样的问题:MySQL中datetime、timestamp类型的列,Java与MySQL时间不一致。
在Java的数据库配置url参数后面加serverTimezone=GMT%2B8,问题就解决了,但具体是什么导致的这一问题呢?
其实,Java与MySQL时间不一致主要是因为:CST时区的混乱问题。
CST是一个混乱的时区,它有四种含义:
美国标准时间 Central Standard Time (USA):UTC-06:00(或UTC-05:00)
澳大利亚标准时间 Central Standard Time (Australia):UTC+09:30
中国标准时 China Standard Time:UTC+08:00
古巴标准时 Cuba Standard Time:UTC-04:00
CST在Linux、MySQL、Java中的含义:
Java中CST时区的分析:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 完整时区ID与时区描述:一共628个
String[] ids = TimeZone.getAvailableIDs();
for (String id : ids) {
// System.out.println(id+"\t"+TimeZone.getTimeZone(id).getDisplayName());
}
// 系统默认时区
TimeZone defaultTimeZone = TimeZone.getDefault();
System.out.println("系统默认时区:"+defaultTimeZone.getID()+"\t"+defaultTimeZone.getDisplayName());
// 北京时区
TimeZone bjTimeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone("Asia/Shanghai");
System.out.println("北京时区:"+bjTimeZone.getID()+"\t"+bjTimeZone.getDisplayName());
// 东京时区
TimeZone djTimeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone("Asia/Tokyo");
System.out.println("东京时区:"+djTimeZone.getID()+"\t"+djTimeZone.getDisplayName());
// CST时区
TimeZone cstTimeZone = ZoneInfo.getTimeZone("CST");
System.out.println("CST时区:"+cstTimeZone.getID()+"\t"+cstTimeZone.getDisplayName());
Date date = new Date(0L);
System.out.println("时间戳=0对应系统时间:"+date.toString());
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
sdf.setTimeZone(bjTimeZone);// 设置北京时区
System.out.println("时间戳0对应北京时间:" + sdf.format(date));
sdf.setTimeZone(djTimeZone);// 设置东京时区
System.out.println("时间戳0对应东京时间:" + sdf.format(date));
sdf.setTimeZone(cstTimeZone);// 设置CST时区
System.out.println("时间戳0对应CST时间:" + sdf.format(date));
}
控制台输出:
系统默认时区:Asia/Shanghai 中国标准时间
北京时区:Asia/Shanghai 中国标准时间
东京时区:Asia/Tokyo 日本标准时间
CST时区:CST 中央标准时间
时间戳=0对应系统时间:Thu Jan 01 08:00:00 CST 1970
时间戳0对应北京时间:1970-01-01 08:00:00
时间戳0对应东京时间:1970-01-01 09:00:00
时间戳0对应CST时间:1969-12-31 18:00:00
由输出可知:
CST在Java中(TimeZone中的CST)表示的是中央标准时间(美国标准时间)
但需注意:Date中的CST是表示的中国标准时间
时间戳永远指的是UTC/GMT的值,同一时间戳在不同时区表示不同的绝对时间
中国的时区ID为Asia/Shanghai。
为了照顾到各地区的使用方便,又使其他地方的人容易将本地的时间换算到别的地方时间上去。有关国际会议决定将地球表面按经线从南到北,划成24个区域,并且规定相邻区域的时间相差1小时。
但由于国家常常是跨越多个时区的,为了照顾到行政上的方便,所以通常国家都会定义一个统一标准际的时区来使用,如中国就是统一使用东八区时间标准(北京时间)。
因为时区众多,所以需要一个标准时间作为基准:
由于地球在它的椭圆轨道里的运动速度不均匀,这个时刻可能和实际的太阳时相差16分钟,地球每天的自转是有些不规则的,而且正在缓慢减速。所以,GMT(格林尼治标准时间)已经不再适合被作为标准时间使用。而是UTC(协调世界时)是原子时秒长为基础,更合适。UTC在时刻上尽量接近于GMT,这两者几乎是一样的。
UTC这套时间系统被应用于许多互联网和万维网的标准中,例如,网络时间协议就是协调世界时在互联网中使用的一种方式。
绝对时间与本地时间关系:绝对时间 = 本地时间 & 时区偏移量 (AbsoluteTime = LocalDateTime & Offset)
绝对时间(AbsoluteTime)是一个指向绝对时间线上的一个确定的时刻,不受所在地的影响。
UTC时间就是一个绝对时间。
当我们记录一个时间为1970-01-01T00:00:00Z(UTC描述时间的标准格式)时,这个时间的定义是没有任何歧义的,在地球上的任何地方,他们的UTC时间也一定是相同的。
Unix时间戳也是一个绝对时间。
Unix时间戳的定义与时区无关。时间戳是指从绝对时间点(UTC时间1970年1月1日午夜)起经过的秒数(或毫秒)。无论您使用什么时区,时间戳都代表一个时刻,在任何地方都是相同的。
本地时间(LocalDateTime)是某一时区的时间。
举例:北京时间2022-10-10 08:00:00。
全球分为24个时区,每个时区和零时区相差了数个小时,也就是这里所说的时区偏移量(Offset)。
例如:北京时间2022-10-10 08:00:00,它本身是一个绝对时间,表示成UTC时间是2020-08-24T03:00:00+08:00
时区偏移量 = 地区 & 规则 (Offset = Zone & Rules)
这里的规则(Rules)可能是一个变化的值,如果我们单纯地认为中国的时区偏移量是8个小时,就出错了。
举例说明:
中国其实也实行过夏令时,(1992年之后中国已经没有再实行过夏令时了,所以大家对这个概念并不熟悉)。
因此,一个地区的时区偏移量是多少,是由当地的政策决定的,可能会随着季节而发生变化,这就是上面所说的规则。
MySQL时区相关参数有两个:
在MySQL启动时会检查当前系统的时区并根据系统时区设置全局参数system_time_zone的值。值可以为UTC、CST、WIB等,默认值一般为CST,该值是只读的。
全局时区:mysql服务端使用的时区,可以修改,默认值SYSTEM
mysql> show global variables like "%time_zone%"; +------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------+--------+ | system_time_zone | CST | | time_zone | SYSTEM | +------------------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> set global time_zone = '+9:00'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> show global variables like "%time_zone%"; +------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------+--------+ | system_time_zone | CST | | time_zone | +09:00 | +------------------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
此时查到的time_zone为全局时区
mysql> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
该命令使全局时区的修改立即生效,否则只有等mysql服务重启才会生效。
会话时区:当前会话的时区,默认取全局时区的值,可以修改
mysql> show variables like "%time_zone%"; +------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------+--------+ | system_time_zone | CST | | time_zone | SYSTEM | +------------------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> set time_zone = '+9:00'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> show variables like "%time_zone%"; +------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------+--------+ | system_time_zone | CST | | time_zone | +09:00 | +------------------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
此时查到的time_zone为当前会话时区
本文使用的MySQL驱动为cj驱动。
Java通过MySQL的jdbc驱动连接MySQL服务端:
对于CST,文章上文有提过:
由于Java和MySQL服务端对CST时区的不同解读,最终导致了Java与MySQL时间不一致的问题。
分析mysql的jdbc驱动代码。MySQL驱动创建数据库连接后,会配置此连接的时区:
数据库连接时区的设置:
serverTimezone配置的注意事项:
你或许会发现一个奇怪的事情:貌似我配置的serverTimezone与据库time_zone不是同一时区。但是Java中的存入时间和查询得到的时间明明是一致且正确的,好像和上面描述得不一样呀。
这里需要强调一下,上面所说的时间不一致是指的Java中的时间与MySQL数据库中的时间(并不是Java中的存入时间和查询得到的时间)。
为何Java中的存入时间和查询得到的时间是一致且正确的?
举个例子说明:
serverTimezone=+9(东九区),time_zone=+8:00(东八区),此时准备把Java中的时间"2022-10-15 08:00:00"存入数据库
Java到MySQL的过程,以及MySQL到Java的过程,时间的处理在MySQL JDBC驱动环节。
serverTimezone配置的归纳总结:
虽然配置的serverTimezone与数据库数据库time_zone时区不一致,Java写入后查询得到的时间也是正常的,但MySQL中存的时间已经是错误的了。
时间戳:指1970-01-01 00:00:00(GMT/UTC)起到当前的毫秒数。与时区无关,不同时区同一个时刻的时间戳是相同的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date(0L);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
sdf.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
System.out.println("时间戳0对应时间(UTC):"+sdf.format(date));
sdf.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println("时间戳0对应时间(UTC+8):"+sdf.format(date));
sdf.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println("时间戳0对应时间(UTC+9):"+sdf.format(date));
}
时间戳0对应时间(UTC):1970-01-01 00:00:00
时间戳0对应时间(UTC+8):1970-01-01 08:00:00
时间戳0对应时间(UTC+9):1970-01-01 09:00:00
Java系统时区:Asia/Shanghai(东8区)
JDBC数据库连接时区:serverTimezone=+8
MySQL全局时区:time_zone=+08:00
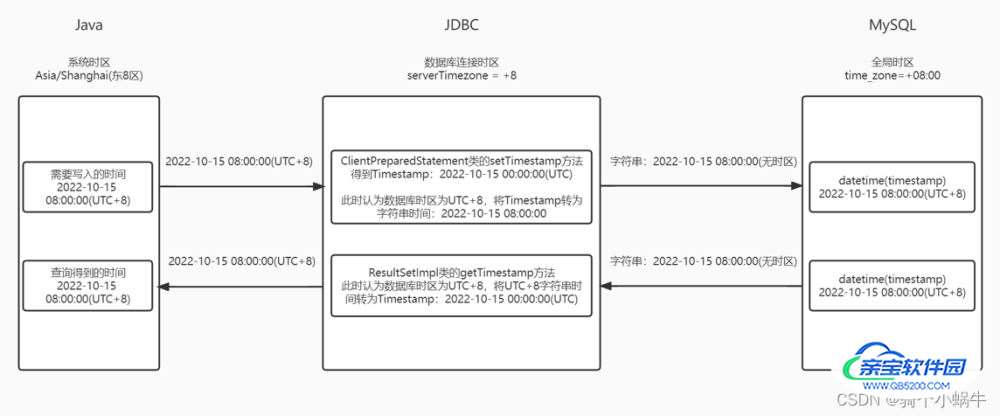
Java系统时区:Asia/Shanghai(东8区)
JDBC数据库连接时区:serverTimezone=-5
MySQL全局时区:time_zone=+08:00
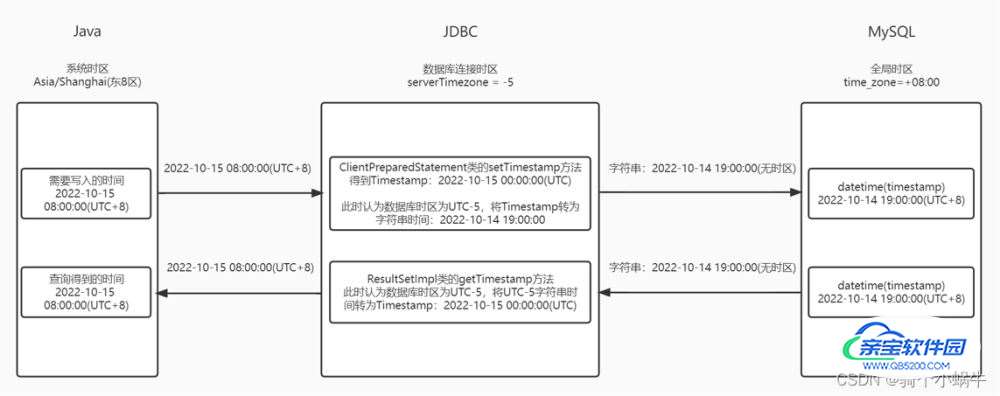
Java写入时间到MySQL服务端环节:
Java准备写入的时间为:2022-10-15 08:00:00(UTC+8)
JDBC先转化得到Timestamp:2022-10-15 00:00:00(UTC)
注意:时间戳记录的是UTC时区的值,与UTC+8时区的2022-10-15 08:00:00是同一时间
JDBC在将Timestamp格式化为UTC-5时区(serverTimezone=-5)的时间字符串:2022-10-14 19:00:00,将字符串传给MySQL服务端
MySQL服务端认为2022-10-14 19:00:00就是MySQL全局时区time_zone=+08:00(UTC+8)时区的时间,存入。
MySQL服务端返回时间给Java环节:
MySQL服务端返回UTC+8时区的时间字符串:2022-10-14 19:00:00
JDBC误认为该时间是UTC-5时区(serverTimezone=-5)先将时间字符串转为Timestamp:2022-10-15 00:00:00(UTC)
Java将Timestamp转化为:2022-10-15 00:00:00(UTC+8)
① JDBC配置MySQL服务时区
如果配置了serverTimezone,则会使用serverTimezone配置的时区
如果没配置,会去取数据库中time_zone变量所配置的时区
具体方法:NativeProtocol类的configureTimezone方法
public void configureTimezone() {
String configuredTimeZoneOnServer = this.serverSession.getServerVariable("time_zone");
if ("SYSTEM".equalsIgnoreCase(configuredTimeZoneOnServer)) {
configuredTimeZoneOnServer = this.serverSession.getServerVariable("system_time_zone");
}
// 获取serverTimezone配置的时区(PropertyKey.serverTimezone=serverTimezone)
String canonicalTimezone = getPropertySet().getStringProperty(PropertyKey.serverTimezone).getValue();
if (configuredTimeZoneOnServer != null) {
// 如果没配置serverTimezone,获取数据库中time_zone变量的时区
if (canonicalTimezone == null || StringUtils.isEmptyOrWhitespaceOnly(canonicalTimezone)) {
try {
canonicalTimezone = TimeUtil.getCanonicalTimezone(configuredTimeZoneOnServer, getExceptionInterceptor());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
throw ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, iae.getMessage(), getExceptionInterceptor());
}
}
}
if (canonicalTimezone != null && canonicalTimezone.length() > 0) {
// 设置服务时区
this.serverSession.setServerTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone(canonicalTimezone));
if (!canonicalTimezone.equalsIgnoreCase("GMT") && this.serverSession.getServerTimeZone().getID().equals("GMT")) {
throw ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, Messages.getString("Connection.9", new Object[] { canonicalTimezone }),
getExceptionInterceptor());
}
}
// 设置默认时区
this.serverSession.setDefaultTimeZone(this.serverSession.getServerTimeZone());
}
JDBC创建数据库连接就是使用该时区。
如果没配置serverTimezone,获取数据库中time_zone变量的时区为CST,就会有问题,因为在java中:TimeZone.getTimeZone("CST")表示的是中央标准时间(美国标准时间)UTC-5(UTC-6)。
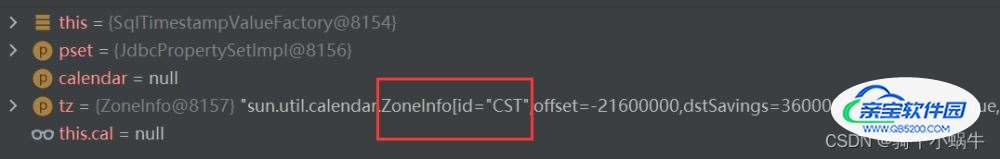
CST问题的源头:
public SqlTimestampValueFactory(PropertySet pset, Calendar calendar, TimeZone tz) {
super(pset);
if (calendar != null) {
this.cal = (Calendar) calendar.clone();
} else {
this.cal = Calendar.getInstance(tz, Locale.US);
this.cal.setLenient(false);
}
}
debug结果:
② Java写入时间到MySQL服务端
ClientPreparedStatement类的setTimestamp方法
@Override
public void setTimestamp(int parameterIndex, Timestamp x) throws java.sql.SQLException {
synchronized (checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) {
((PreparedQuery<?>) this.query).getQueryBindings().setTimestamp(getCoreParameterIndex(parameterIndex), x);
}
}
ClientPreparedQueryBindings类的setTimestamp方法
public void setTimestamp(int parameterIndex, Timestamp x, Calendar targetCalendar, int fractionalLength) {
if (x == null) {
setNull(parameterIndex);
} else {
x = (Timestamp) x.clone();
if (!this.session.getServerSession().getCapabilities().serverSupportsFracSecs()
|| !this.sendFractionalSeconds.getValue() && fractionalLength == 0) {
x = TimeUtil.truncateFractionalSeconds(x);
}
if (fractionalLength < 0) {
fractionalLength = 6;
}
x = TimeUtil.adjustTimestampNanosPrecision(x, fractionalLength, !this.session.getServerSession().isServerTruncatesFracSecs());
// 将时间戳格式化为字符串时间
// this.session.getServerSession().getDefaultTimeZone() 时区(未配置serverTimezone,且数据库中time_zone变量的时区为CST时,这里就是CST时区)
this.tsdf = TimeUtil.getSimpleDateFormat(this.tsdf, "''yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", targetCalendar,
targetCalendar != null ? null : this.session.getServerSession().getDefaultTimeZone());
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append(this.tsdf.format(x));
if (this.session.getServerSession().getCapabilities().serverSupportsFracSecs()) {
buf.append('.');
buf.append(TimeUtil.formatNanos(x.getNanos(), 6));
}
buf.append('\'');
setValue(parameterIndex, buf.toString(), MysqlType.TIMESTAMP);
}
}
将时间格式化为字符串时间(根据连接的时区)。
③ MySQL服务端返回时间给Java
ResultSetImpl类的getTimestamp方法
public Timestamp getTimestamp(String columnName) throws SQLException {
return getTimestamp(findColumn(columnName));
}
public Timestamp getTimestamp(int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
checkRowPos();
checkColumnBounds(columnIndex);
return this.thisRow.getValue(columnIndex - 1, this.defaultTimestampValueFactory);
}
SqlTimestampValueFactory类的localCreateFromTimestamp方法
public Timestamp localCreateFromTimestamp(InternalTimestamp its) {
if (its.getYear() == 0 && its.getMonth() == 0 && its.getDay() == 0) {
throw new DataReadException(Messages.getString("ResultSet.InvalidZeroDate"));
}
synchronized (this.cal) {
try {
// 这里就是关键环节,this.cal是一个Calendar类,里面有时区信息(未配置serverTimezone,且数据库中time_zone变量的时区为CST时,这里就是CST时区)
this.cal.set(its.getYear(), its.getMonth() - 1, its.getDay(), its.getHours(), its.getMinutes(), its.getSeconds());
Timestamp ts = new Timestamp(this.cal.getTimeInMillis());
ts.setNanos(its.getNanos());
return ts;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}